This content was adapted from Andrea Fryrear’s 90 minute MarketingProfs webinar “Agile Project Management for Marketers” and updated in April 2024.
“There is absolutely no risk or dependency here. This is a straightforward project.” - No project manager ever
Projects never, ever turn out this way, yet we consistently plan as if they will. Definition of insanity anyone?
Traditional project management focuses on heavy up-front planning to mitigate uncertainty, but the best laid plans don't survive first contact with the real work of completing the project. That's why, instead of pulling their hair out like their project manager predecessors, modern PMs are turning to a methodology that seems to have worked process wonders for their colleagues in the IT department: Agile project management.
The Beginnings of Agile Project Management
Agile is a methodology that was created to help teams and individuals:
- Create plans that help them achieve goals in the long term
- Iterate more readily over the course of projects
- Isolate failure to the early parts of the production process as opposed to the end
- Be more productive without changing the amount of available resources, such as time and money
As marketers, we often have our hands on lots of different projects. We really need to get things done more efficiently and (hopefully) with less drama. So a shift towards a truly Agile work process can make a huge difference to our productivity. In this article, we'll touch on the foundational ideas behind agility and how we can make them work for managing projects in the marketing context.
We'll look at some cornerstone concepts of Agile, such as applying frameworks, building a backlog, reducing waste, and preventing context switching. As a result, you’ll be armed with actual takeaways to use, regardless of what projects you’re working on or what type of marketing team you’re part of.
Agile Project Management Frameworks & Values
In the world of software and IT, Scrum is the most popular Agile framework. It involves organizing sprints - two to four weeks long - with bursts of active work during that time frame. In this period, teams continually release value as they work through their tasks. After the completion of all items, the team members review and plan the next burst of active work.
On the other hand, the alternative Agile framework, called Kanban, does not use sprints. Kanban helps work flow through the system smoothly by keeping task execution, review, and planning continuous.
Scrumban is our own little hybrid. During our trainings with AgileSherpas, as well as in our research, we’ve discovered that most marketing teams prefer using aspects of both frameworks together. In fact, our own surveys found this to be the case for 6 consecutive years. However, the 7th annual State of Agile Marketing Report actually found equal use of Scrum, Kanban, and hybrid frameworks.
That said, neither Scrum, nor Kanban were originally created with marketers in mind. The former comes from the realm of software development, the latter from the land of manufacturing. We still believe that combining elements of both for a custom approach provides the best results for marketers.
Agile Values Before Agile Frameworks
Even if the frameworks weren’t built for marketers specifically, there are a number of Agile values that are very relevant to marketing. We can focus on them in order to make a better decision about which framework we might use with our team. In marketing terms, the Agile values that most apply to marketers are:
- Value individuals and interactions over processes and tools. In other words -- if we can get everyone in a room for shared understanding, that’s better than spending months putting together the perfect Gantt chart.
- Viable campaigns over huge marketing plans that are probably out of date a couple of days after we finish them
- Do something relatively small and experimental that we can learn from and then improve over time instead of putting all of our eggs in the same basket
- Be customer-centric, rather than sticking to the hierarchies and silos that we’ve developed internally
- We have a project plan to follow, but when we have a good indicator that adjustments need to be made, we make them rather than following a plan blindly.
So, even if you haven’t chosen an Agile framework yet, encouraging these values among your team members will get you there.
Release Faster with Minimum Valuable Projects
Nearly all PMs have experienced projects that get delayed over and over because something just isn’t quite perfect. This translates into costly delays not just because the project takes too long to get completed but because these delayed projects don’t get actual real-world feedback for far too long.
That’s why Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) are an essential part of Agile project management. They're crucial to the values of iteration, experimentation, and being customer-centric. For Agile project management, we might rephrase slightly and call them Minimum Viable Projects.
Marketers often assume that MVPs don’t really apply to them, but they can and should be used to test ideas and minimize what we need to invest to learn valuable lessons. However, there seem to be some misconceptions about what an MVP is and how it can relate to project management.
MVP: The bad definition
“The minimum viable product is not quite the crappiest thing you could possibly release.” This definition neglects the criteria that MVPs should still be providing value to the audience you want to reach.
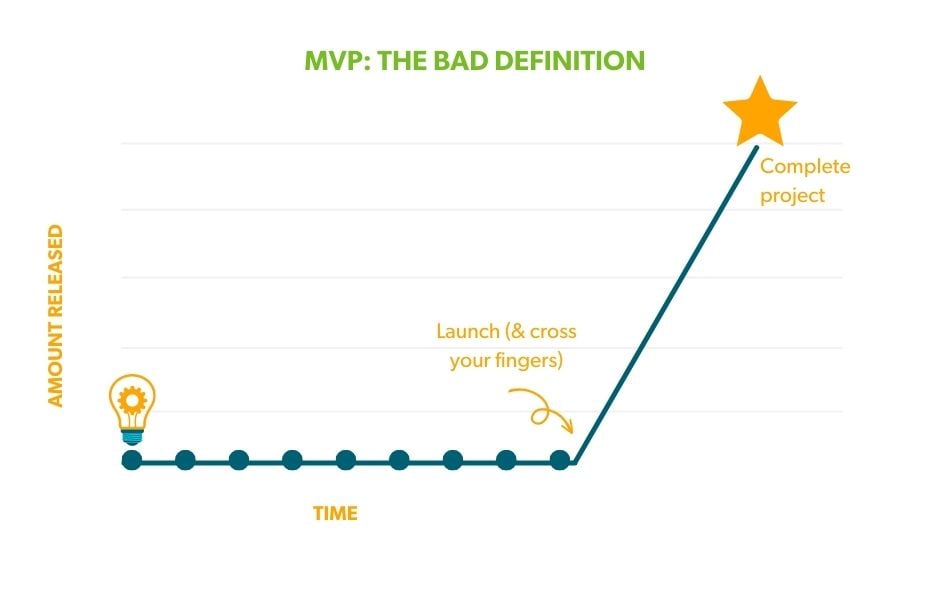
When we take this approach, we get situations like this: 
In this example we are not:
- providing a functional MVP
- learning over the course of the process
- making any adjustments to our original hypothesis
- delivering value to our customer until the very end of the process
- taking a low-risk approach
Good Definition #1
A better definition of the MVP is that “the minimum viable product is the smallest product release that successfully achieves its desired outcomes.” It represents the smallest subset of work we could release that still delivers value, but is not the whole complete piece of work.
Good Definition #2
Further, “a minimal viable product is also the smallest thing you could create or do to prove or disprove an assumption.” With both ‘good’ definitions of an MVP at the center of our work, we are able to provide value to our customers much sooner.
As in this example: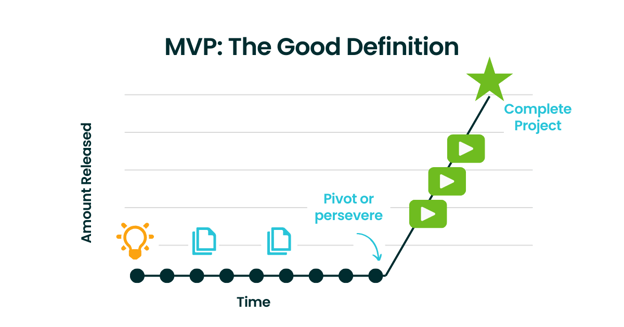
The iterative approach can help us make decisions very early on, as opposed to waiting until the end of the process. In the marketing context, we can validate the idea and iterate as we go to WOW our customers.
The Agile Project Management Triangle
Most PMs are familiar with the basic idea of the iron triangle, a visualization of the way Scope, Resources, and Time interact with each other in projects. Anything that affects one will inevitably affect the others as well, meaning we must always consider the tradeoffs.
However, these three areas are also not equal in traditional waterfall methodologies, as scope tends to be fixed while the resources and time needed to achieve that scope are merely estimates.
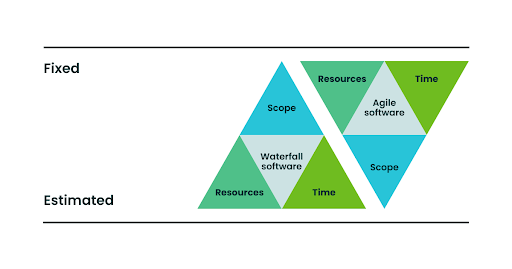
But in Agile project management, it’s usually the opposite. The time and resources we have tend to be fixed while the scope of work is estimated. In other words, instead of throwing whatever we have at a project to eventually achieve the intended scope, Agile focuses more on using those resources to deliver the most value possible.
All of this can change when you’re looking at longer-term planning, but this is generally a helpful way to visualize a key difference between traditional and Agile project management.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Slicing of Work
We can also approach Agile marketing project management by slicing up our work differently. 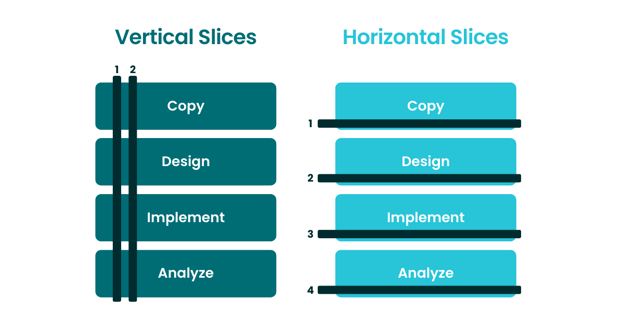
A vertical slice takes components of all four of our typical marketing process phases and delivers them as a subset of all. On the other hand, the horizontal slicing approach means that we’re releasing each piece separately. We wait a long time. In the end, the whole project is totally done before we give anything over to anybody.
It’s a different way of executing work, which is slower, less effective, and does not allow for iteration. As you iterate on your marketing campaigns, keep in mind -- it’s not iteration if you only do it once.
The MVP shouldn’t be your team’s final product. In fact, it should be one of many MVPs on the road to the most valuable piece of work you can produce. Iterations just help us get to our best work in a lower risk and faster way.
Visualizing Project Work With a Backlog
Once you begin to design projects in a conducive way to your new iterative approach, your team can begin to incorporate Agile project management practices into the iterations that are carried out. First, we need to have visibility in the work we do. This is a core tenet of any Agile implementation and particularly important and useful for remote teams.
One of the most powerful tools in the Agile toolbox for improving visibility within a team is the backlog. In a traditional approach to the marketing process, we would build out the original marketing plan with the idea that we know all the details and they won’t change. The schedule, the requirements, the timing -- everything gets mapped out with great certainty. But when do we really know everything about our marketing plans right off the bat?
In reality, we all live in a volatile, digital world in which this type of certainty in planning would never happen. That's why, in an Agile marketing team, we aim to create backlogs of work that we are continually molding depending on the opportunities we want to pursue.
Backlogs are smaller, more adaptable plans that we can iterate upon as we move forward and release smaller batches of work. These batches allow us to learn, which gives us an opportunity to change ourselves depending on the opportunity. Consider the backlog as a prioritized to-do list.
The backlog approach to planning work allows marketing teams to deal with changing priorities or scope of a project. Unlike in the traditional marketing context, when saying “I’ll put it in my backlog” means a task will be ignored forever, Agile backlogs are very active and current.
Having a "DEEP" Backlog
For the backlog to be at its best, it needs to be DEEP:

Detailed, meaning it contains enough information about the work items (such as requirements and specifications)
Emergent, meaning it's up-to-date and always gets adjusted if it's not.
Estimated, meaning it contains information about how much effort each item in it requires. This helps the team and the project manager prioritize.
Prioritized, meaning the most important items are the ones at the top.
This makes it different from a to-do list. In the backlog, there can only be a single top priority that the team is collectively focused on.
Categories of a Project Backlog

The tasks in the Up Next category need to be detailed enough so that the person responsible can start working on it immediately. In some cases, this may mean that stakeholders have already been consulted to get their requirements and all necessary resources are in place. But this helps avoid the classic problem of people sitting around waiting for more information so they can start a task, particularly problematic in this new era of remote work.
Coming Soon is a section of the backlog reserved for tasks that will be worked on further into the future. These work items don’t need to be as detailed.
Someday contains work items the execution of which may be uncertain. These may not end up in the scope of the final project or may be de-prioritized as the project evolves. We don’t want to spend time on these lower priority items.
Deadlines in the Project Backlog
Work items in the backlog can also have deadlines which can be one of the criteria for prioritizing by the project manager.
However, in the best case scenario, the biggest driver of work being done sooner rather than later should be its value, not its deadline. We want to do the most valuable things first.
The Challenges of Estimation
Every project manager should be well aware of just how bad we humans are at estimating how long work will take. These inaccurate estimates lead to all sorts of problems as we end up taking on too much work or disappointing stakeholders who expected work sooner.
This is why, as you build a backlog and especially if you choose to work in sprints, accurate estimation helps you avoid overburdening the team or delivering work late. One effective way to improve the quality of your estimations over time is through games like planning poker that gamify the process.
Reducing Waste and Limiting WIP During a Project
If your backlog is ready to go, your marketing team can start processing the work items in it. This is where the Lean and Kanban concepts come in to help us get more done in less time.
Removing Waste from Your Project
The principle of Lean is all about getting rid of the parts of our process that do not add value, so our team can free up capacity to focus on the more valuable things.
There are many aspects of the process that don't create any value, also called waste, and sometimes they aren't easy to spot. Making them visible helps us identify, and remove what’s unnecessary so we make room for more valuable activities.
In Lean, there are 8 Categories of Waste. We’ve adapted them to the marketing context here:
- Unplanned work: Context switching, starting not finishing, inability to say “no”.
- Neglected work: We can’t work on this now because we’re working on this other thing.
- Over-processing: Over-engineering a simple task, spending too much time working on something with less value, and manual processes that could be automated.
- Motion: Unnecessary meetings, procrastination, hunting down stakeholders.
- Waiting: Being idle because external or internal dependencies block your progress.
- Unknown dependencies: Coordination needs are high, people aren’t available when you need them, and a change in one part changes the whole project.
- Conflicting priorities: All meetings and no work, taking on new requests before finishing old ones, squeaky wheel syndrome.
- Too much WIP: Too much work in progress
Our team’s goal should be to get waste out, so that value can go up.
Using a Kanban Board to Run a Project
One way we can get more visibility into the work that we do is to use a Kanban board to visualize our work items. In their simplest version, Kanban boards take on this structure: 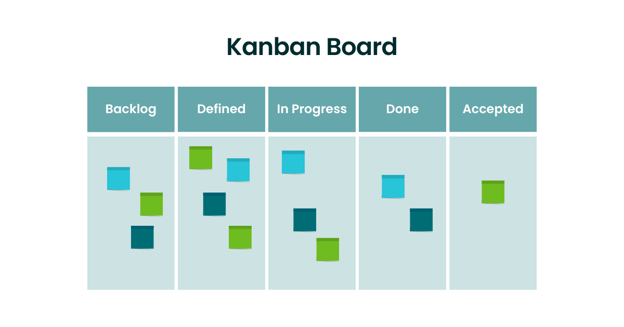
To build your team’s board, ask yourself:
- What are the stages of the process that a work item needs to go through to be considered done? Map these out as columns.
- Where are the handoffs between individuals, teams or departments?
If your Kanban board accurately reflects your Agile project management process, it’ll become a radiator of information about your project progress.. Everyone on the team, involved in the project should be interacting with this board and any stakeholder or team member should be able to walk up to it and understand how this project is going. The board should include essential information such as:
- Who owns which tasks?
- Which task is blocked and cannot move forward in the process?
Below is a more sophisticated version of a Kanban board. This board includes swimlanes that separate the types of work we do and add even further granularity. 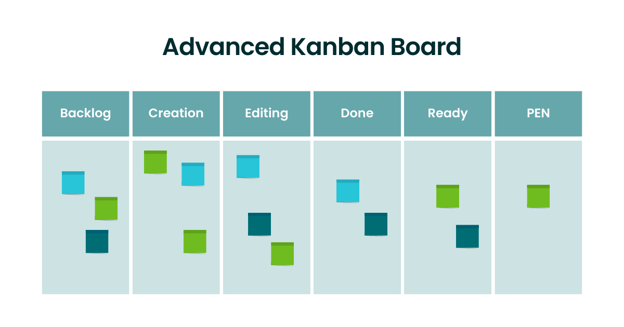
Adding WIP Limits
Once we have a Kanban board created, we can start applying work in progress limits to the appropriate process sections. Work in progress (WIP) limits help our marketing teams stop starting and start finishing our tasks. 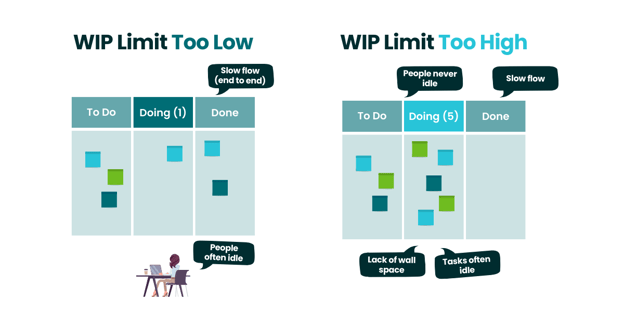
Ironically, the outcome is the same when your WIP is too low or too high: it takes way too long to get work released from the system. When the WIP limit is too high (or you don't have one), things take too long to get done because we literally can't work on several things at the same time, so we jump back and forth.
The result is that tasks get stuck. They aren't being worked on, even when marked "doing." Instead, we need to find a WIP limit that’s just right. The perfect WIP limits mean work items aren’t idle in the process and everyone on the team is working on something.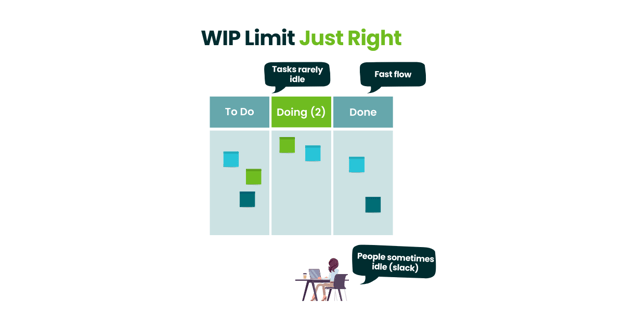
WIP limits and slack time
It’s OK to be idle once in a while! During these moments of "slack," team members have an opportunity to cross-train amongst themselves, learn some additional skills for the next iteration of work, or talk to someone for the purpose of knowledge sharing.
Remember that trying to work at 100% capacity all the time is a recipe for burnout, higher attrition, and an inability to handle any crisis that may arise.
In more advanced Kanban boards that use work in progress limits to regulate the pace of work, team members can:
- Set up a limit for the whole board. For example, "our board can only have 10 things in it, no matter what stage they’re in."
- Set up WIP limits per person. For example, "each person can only be allowed to commit a maximum of two work items at a time."
WIP limits are important for marketing project management in particular, because they can help us focus on important work and not burn out by the end of the week.
Agile Project Management Tackles Context Switching
WIP limits are really helpful in alleviating context switching, which isn’t just a marketing problem. It’s an issue in all types of knowledge work. We used to call it multitasking, but now we know that we actually switch back and forth between different work or projects.
What we don’t consider is that it can take us more than 26 minutes to get back into a productive flow of work once we're interrupted. This act of jumping around creates enormous amounts of waste in any project, and should be avoided by project managers at all costs.
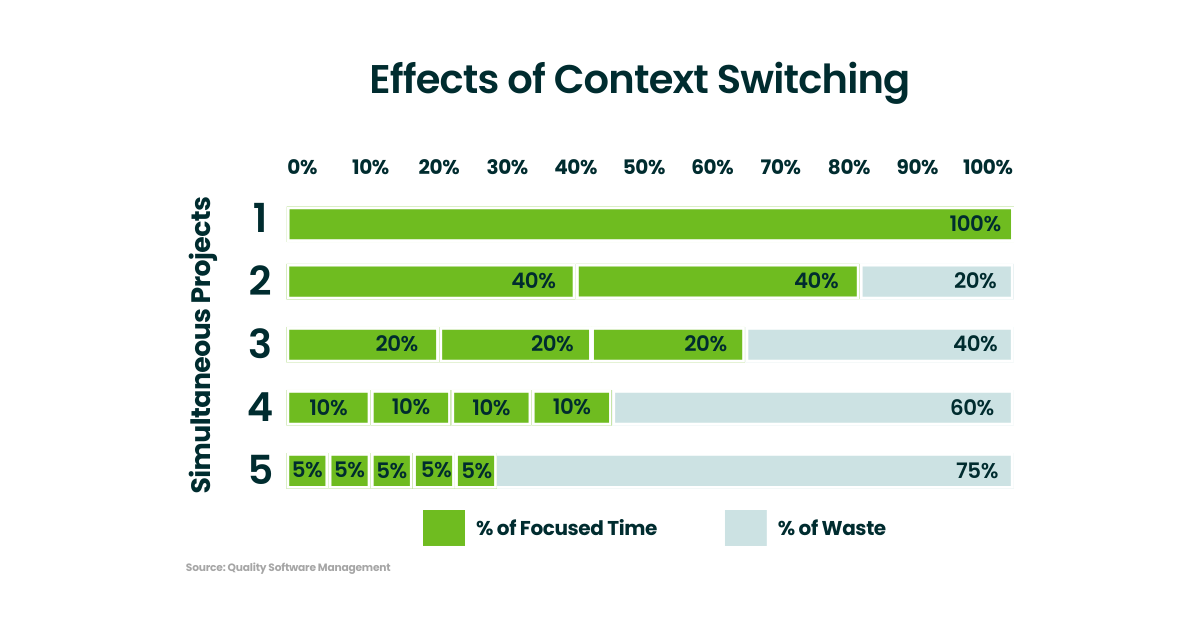
We also get interrupted…a lot. This prevents us from getting important work done.
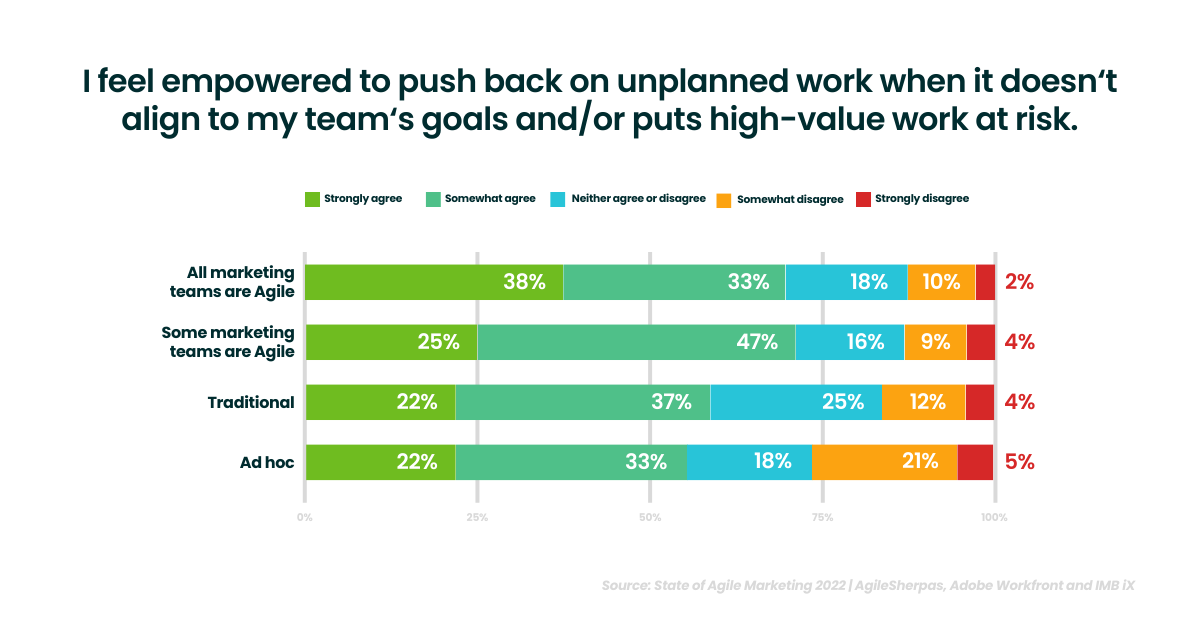
Saying “no” is a big problem with marketers also. They either do not have the authority or the autonomy to say “no” to taking on new work items.
This leads to excessive work in progress, lots of context switching, and projects that go way over the deadline. To prevent issues like this, we need to put WIP limits in place and be diligent in adhering to them.
Fortunately, 38% feel empowered to push back on unplanned work when it doesn’t align with the team’s goals or puts high-value work at risk.
Executing Agile Project Iterations with Scrum
What do we do to help the project get better over time?
Using a Scrum system for our Agile project management allows us to continually iterate on the project and improve it as we go.
The Structure of Scrum
Scrum is a framework for managing a process that can be Agile. Using Scrum does not automatically make a team Agile. Our teams still need to focus on developing the Agile mindset among their members to make Scrum work for them. The elements of a Scrum-based process include: 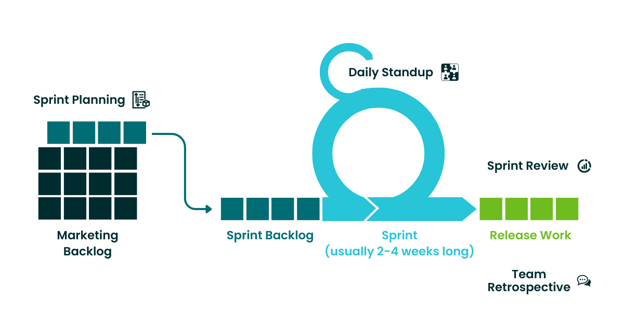
A marketing backlog, from which the team pulls work before the beginning of a sprint. Sprints are periods of time during which the team actively works on tasks from the backlog. This spurt of work can be anywhere from 2-4 weeks in duration. It is recommended to keep sprints as close to 2 weeks as possible. Otherwise, each sprint becomes too big and more difficult to manage. Each day during the sprint, the team has a daily standup meeting that helps them sync priorities on a regular basis.
At the end of the sprint, there’s a valuable piece of releasable work ready to be delivered to the customer.
Scrum Meetings
The Scrum framework helps teams avoid excessive meetings. However, there are a few mandatory meetings that any practicing Scrum team should respect, such as:
- Sprint planning
- Daily standups
- Sprint review
- Retrospective
During the sprint planning, the members of the team decide what work items they’ll commit to tackle in the coming sprint.
The daily standup meeting is an extremely brief daily meeting that keeps the team on track over the course of the sprint.
Another preferred format for the daily standup uses the team Kanban board to lead the meeting and addresses the following questions:
- What cards got done?
- What cards got started?
- Which cards are blocked and why?
At the end of the sprint, we have two different meetings that marketers like to conflate. Company members who aren’t working on the project can come in to join the Sprint Review to see the finished work. 
The retrospective meeting is dedicated to the internal team only. It is a time when they can ask themselves -- what should we change to make the next sprint go better? 
Disclaimer: The retro is not useful when it’s 4pm on a Friday and we stare at each other for 10 minutes before agreeing to get a beer and go home. Get your team in a room for at least an hour to talk about what is working or not working with the process, not the work.
Roles in Scrum
Scrum also assigns roles to team members who are responsible for process improvements and keeping the backlog up-to-date.
These roles are:
- Scrum Master: supports process improvement & impediment removal; facilitates meetings
- Marketing Owner: owns the backlog; combines strategic perspective with deep understanding of the team; “last wringable neck”
- Developer/Marketer: No hierarchy within the team; ideal = extremely cross functional, i.e anyone could pick up any task
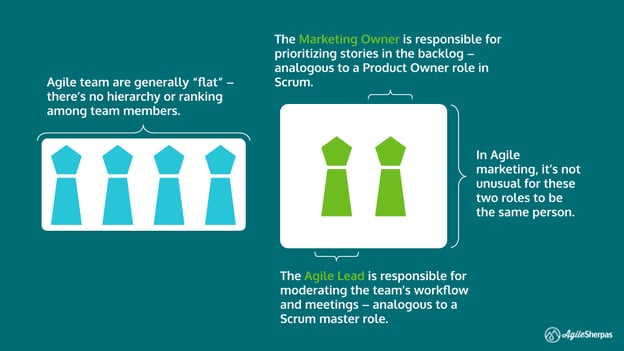
Disclaimer: In the marketing world, we often combine the Scrum Master and Marketing Owner role and assign it to a single member of the team. That works (if you do it right)! Problems tend to arise when that person is also trying to do work as a member of the general team. Owning the backlog, making improvements to the process structure as well as pulling items from the backlog can be too much for one team member to handle at once.
Work “Burns Down” During a Scrum Sprint
If your backlog is estimated, then you will be able to track as work gets completed during the sprint. Throughout the sprint, the work burns down to 0, that’s why we keep an eye on its pace on, what is called, a burndown chart. 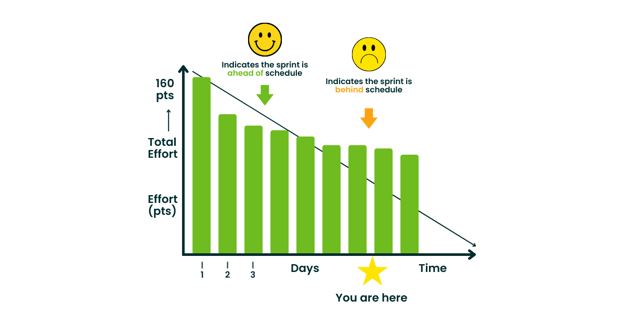
If this brief introduction to a few of the most essential Agile project management concepts have encouraged you to try running one of your upcoming marketing projects using Agile practices -- use this quick checklist as you set up your first Agile project.
- Commit to Agile values: Ensure your team understands that you’ll be using an Agile approach and what that means.
- Identify your MVP: What can you release that’s lower risk but still adds value?
- Visualize the work: Use a backlog and a Kanban board (digital or physical) to keep tabs on what the team is working on.
- Limit WIP and embrace “no”: Help the team reduce their context switching and empower them to say “no” and/or “not right now".
- Use Sprints to iterate: Build on your MVP by adding additional value/beauty/functionality to your project using Scrum and recurring Sprints.
Make sure your team can maximize these five points as a continuous part of your daily workflow. Not sure how to do that?
This Agile Marketing Fundamentals course has everything you’ll need to get a firm grasp of the essentials. Working with seasoned Agile coaches, you’ll have ample opportunity to ask questions to really understand how to apply these concepts to your specific situation. Best of all, you end up with a valuable certification at the end.




